World IBD Day Sheds Light on the Connection between IBD and Liver Health
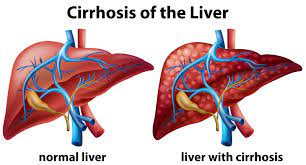
May 19th marks World IBD Day, a day dedicated to raising awareness about inflammatory bowel disease (IBD). This year, the focus is on the connection between IBD and liver health. According to the IBD Society, up to 30% of people with IBD may develop liver disease, which can range from mild inflammation to severe scarring. The European Crohn’s and Colitis Organisation (ECCO) adds that liver disease is more common in people with Crohn’s disease than those with ulcerative colitis. “Many people with IBD are not aware of the potential impact on their liver health,”. “It’s important for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to monitor liver function and catch any issues early.” The Crohn’s and Colitis Foundation (CCF) India also emphasizes the importance of early detection and treatment. “Liver disease can be silent and asymptomatic in its early stages, which is why regular check-ups are crucial,” In addition to regular check-ups, maintaining a healthy lifestyle can also help protect liver health in people with IBD. This includes avoiding alcohol, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular exercise. “World IBD Day is an opportunity to raise awareness about the impact of IBD on liver health and the importance of early detection and prevention,” . “By working together, we can improve outcomes for people living with IBD and liver disease.” For more information about World IBD Day and the connection between IBD and liver health, visit (website) https://drchetankalal.com/
World IBD Day Sheds Light on the Connection between IBD and Liver Health Read More »