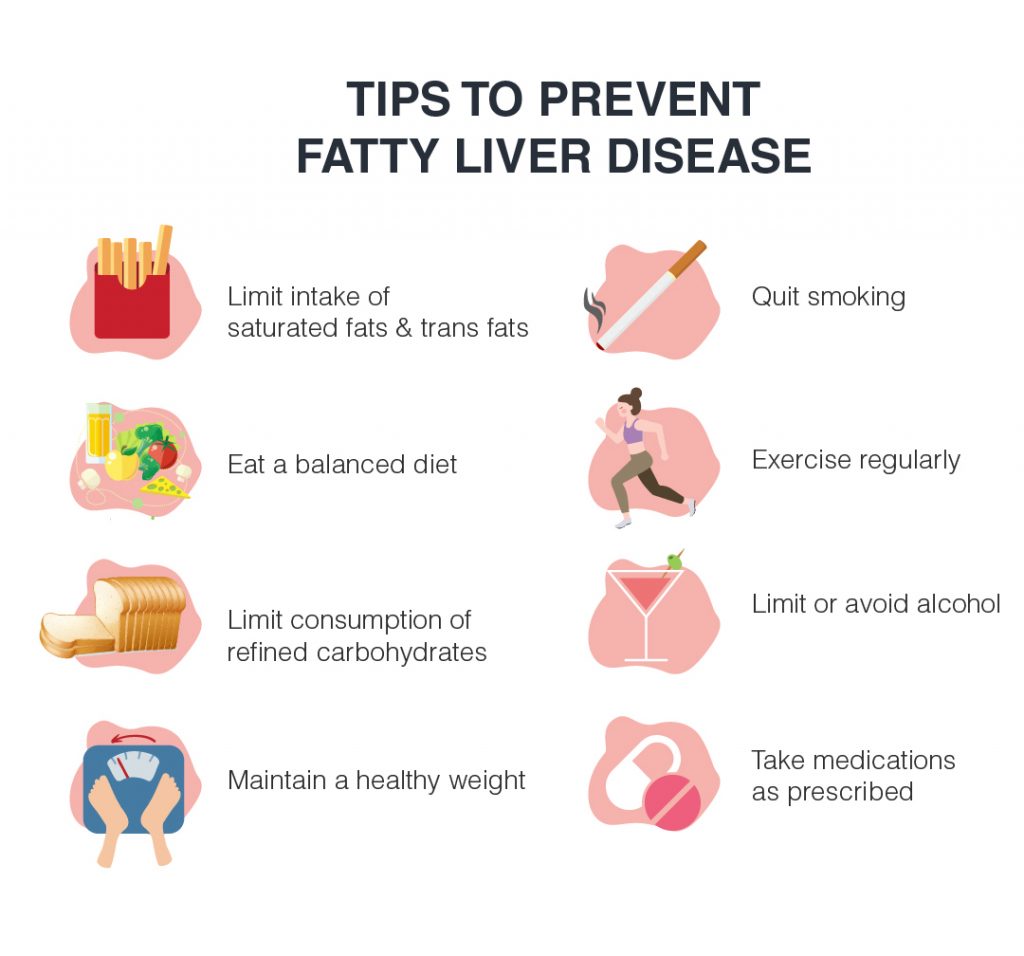
Fatty liver, also known as steatosis hepatitis, is a condition where fat accumulates in the liver. It can lead to more serious conditions like inflammation and cirrhosis if left untreated. The best way to prevent fatty liver is to make lifestyle changes that reduce your risk factors for developing it. First, you should eat a healthy diet low in saturated and trans fats and high in fibre, fruits, and vegetables. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugar-sweetened beverages, red meat, fried foods, and other foods high in calories or unhealthy fats. Eating smaller meals throughout the day can help you maintain a healthy weight and reduce fat build-up in the body. Second, exercise regularly. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate physical activity per day or 150 minutes per week; this will help you maintain a healthy weight while improving overall health markers such as blood pressure and cholesterol levels. Additionally, regular physical activity can help reduce stress levels which may contribute to fatty liver disease progression by increasing inflammation levels within the body. Thirdly abstain from alcohol consumption if possible as alcohol use has been linked with an accumulation of fat within the liver cells which could potentially lead to steatosis hepatitis (fatty liver). If you do choose to drink alcohol then limit your intake since heavy drinking over prolonged periods of time is associated with increased risk factors for developing the fatty liver disease (FLD). Finally, if you are obese or overweight then try to work towards reducing your body weight through dieting and exercise. This will not only improve overall health markers but also reduce abdominal fat which has been found to increase risk factors associated with FLD such as insulin resistance, inflammation, etc. Furthermore talk with your doctor about any medications that could be potentially damaging particularly that related to diabetes, high blood pressure, etc. since these have been linked with fatty liver disease progression.